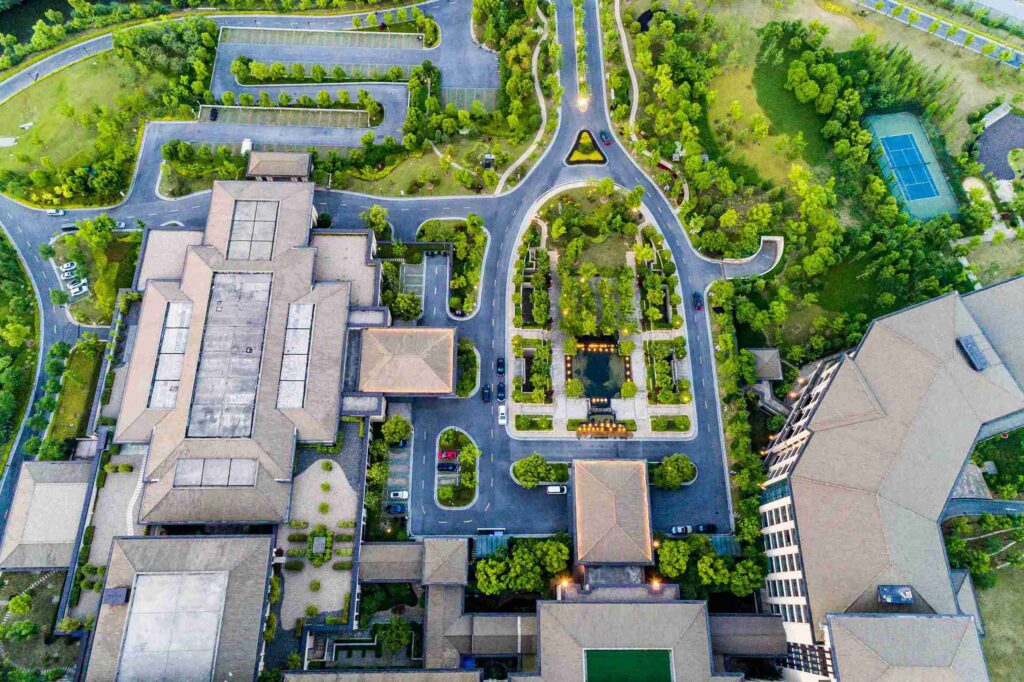
The New Suburban Frontier
Across the United States and globally, the definition of a “city” is evolving. What were once traditional suburban communities built for low density and car dependency are now becoming testing grounds for the next wave of smart urban development. Instead of focusing solely on major metropolitan cores, developers are turning their attention to the new frontier: suburban regions with enough land, flexibility, and demand to support smart city innovation.
This shift is not accidental. It reflects a mix of demographic preferences, technological capability, infrastructure needs, and financial feasibility. Remote work, population decentralization, and rising expectations around convenience and digital integration have created fertile ground for smart suburban development.
A growing body of research suggests that developers are increasingly viewing suburbs as more viable than traditional urban centers for implementing smart infrastructure and mixed use master plans. Smart Cities Dive notes that a new generation of “smart suburbs” is emerging as a scalable blueprint for innovation, affordability, and community centered design.
Source: Smart Cities Dive
https://www.smartcitiesdive.com/news/for-some-developers-smart-suburbs-are-the-new-smart-cities/443600/
This next frontier represents one of the most important shifts in real estate and urban planning of the decade.
Quick Data Snapshot
- Over 65 percent of U.S. households now live in suburban areas.
- Remote and hybrid work adoption exceeds 50 percent in major metropolitan regions.
- Demand for walkable, mixed use suburban centers has grown more than 20 percent since 2020.
- More than 70 new master planned communities in the U.S. include smart infrastructure as a core component.
- Digital connectivity and mobility access rank among the top three priorities for relocating families.
- Smart suburban projects have grown nearly twice as fast as smart urban districts between 2021 and 2024.
These metrics illustrate why developers are reimagining suburbs as the next scalable model for integrated, technology enabled communities.
Developer Interest Is Rising
Smart Cities Dive highlights that many developers now see suburban communities as ideal laboratories for innovation because they offer more room for experimentation, more predictable zoning paths, and more opportunity to connect digital systems with physical design.
Source: Smart Cities Dive
https://www.smartcitiesdive.com/news/for-some-developers-smart-suburbs-are-the-new-smart-cities/443600/
Suburban regions also offer a less expensive and less politically complex environment for testing:
- Smart mobility networks
- Autonomous shuttle routes
- Distributed energy systems
- Digital governance tools
- Mixed use district planning
- Walkable “20 minute community” models
A detailed study by SOM shows how 20 minute suburban planning principles can reshape mobility and accessibility. Their analysis demonstrates how suburban regions can provide urban style convenience without urban density.
Source: SOM 20 Minute Suburbs Framework
https://www.som.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/20230223_20minSuburbs-1677186785.pdf
The opportunity extends beyond infrastructure. KPMG’s smart city governance report shows how suburban municipalities can adopt digital solutions faster because their permitting processes are often more agile and less encumbered by legacy systems.
Source: KPMG From Smart to Smarter Report
https://assets.kpmg.com/content/dam/kpmgsites/xx/pdf/2024/11/from-smart-to-smarter-report.pdf.coredownload.inline.pdf
In short, developers are targeting suburbs because the environment allows innovation to scale.
Why Developers Are Pivoting to Smart Suburbs
Returns and Differentiation
Developers are seeking competitive differentiation in a crowded housing environment. Smart suburban projects stand out by offering:
- Integrated mobility networks
- Smart home technology
- Renewable energy systems
- Mixed use walkability
- Community experience design
These qualities command a premium. Buyers and renters increasingly expect digital integration and convenience as part of modern living.
Demand for Experience and Space
Remote work has enabled households to prioritize both lifestyle and livable space. Smart suburbs combine the affordability and space of traditional suburbs with the connectivity and convenience of urban centers. This blend appeals to families, young professionals, and retirees alike.
Feasible Planning Experiments
Unlike large metropolitan cores, suburbs offer:
- Larger parcels
- Faster approvals
- Easier land assembly
- Lower acquisition costs
- Greater flexibility for piloting new tools
Developers can run small district scale experiments before expanding platforms across an entire community.
Developer Playbook — Five Practical Strategies
1. Master Plan for Mixed Uses
The most successful smart suburban communities adopt a master planned approach that blends:
- Residential zones
- Retail nodes
- Employment clusters
- Green spaces
- Community amenities
This integrated model supports walkability and reduces car dependency while offering residents access to daily needs within short distances.
2. Bake In Digital Infrastructure
Digital infrastructure is the backbone of any smart suburban development. Core elements include:
- High speed broadband
- Smart meters
- IoT enabled street lighting
- Integrated mobility apps
- Real time traffic systems
- Cyber security frameworks
By embedding digital systems from the beginning, developers create a scalable backbone for long term community management.
3. Start With High Impact Pilots
Successful smart districts begin with small pilots that demonstrate immediate value, such as:
- Smart parking systems
- Micro transit or shuttle loops
- Green energy microgrids
- Sensor enabled waste management
- Smart water conservation systems
These pilots build community trust and provide proof points for expanding technology adoption.
4. Form Partnerships With Local Government and Utilities
Smart suburban development requires close coordination with:
- Local planning departments
- Utility providers
- Transportation agencies
- Broadband companies
- Public safety departments
Strong partnerships help streamline approvals and ensure that systems integrate seamlessly with regional infrastructure.
5. Measure Outcomes and Communicate Value
Developers must track measurable outcomes, including:
- Traffic reduction
- Energy efficiency
- Water use optimization
- Community satisfaction
- Operating cost savings
Communicating results helps build political and community support for scaling innovation.
Case Examples and Quick Wins
Mall to Main Street Retrofits
Underperforming retail malls are being transformed into mixed use smart districts featuring housing, green corridors, and community hubs. These retrofits unlock large parcels and convert obsolete retail into high value urban style centers.
Master Planned Smart Suburbs
Several new suburban master plans across the U.S. integrate autonomous mobility routes, district energy, shared amenities, and community wide IoT systems. These communities attract both residents and corporate tenants seeking modern, sustainable environments.
Global Flagship Projects
Internationally, projects like Ellinikon in Greece demonstrate how large scale suburban redevelopment can become a global model for smart urbanism. Business Insider’s report shows how this project is transforming an abandoned airport into a vibrant smart city district.
Source: Business Insider Ellinikon Report
https://www.businessinsider.com/ellinikon-greece-athens-abandoned-airport-smart-city-photos-2024-6
Additional global insights can be found in UN Habitat’s smart city outlook, which identifies dozens of emerging suburban regions as next generation innovation hubs.
Source: UN Habitat Smart City Outlook
https://unhabitat.org/sites/default/files/2024/12/un_smart_city_outlook.pdf
JLL’s analysis also highlights global suburban smart districts as crucial for solving housing, sustainability, and mobility challenges at scale.
Source: JLL Smart Cities Insights
https://www.jll.com/en-ae/insights/solving-the-challenges-of-smart-cities
A Six Point Checklist for Underwriting a Smart Suburban Project
1. Parcel Scale and Zoning Flexibility
Developments require parcels large enough to support mixed uses and flexible land use policies that enable innovation.
2. Digital Backbone
Underwriters must evaluate planned broadband deployment, IoT integration, and long term infrastructure maintenance costs.
3. Local Governance Buy In
Smart suburban development depends on alignment with local government priorities and willingness to support pilot projects.
4. Phasing and Pilot ROI
Phased development reduces risk. Early stage pilots should deliver visible returns and operational savings to justify scaling.
5. Community and Affordability Plan
Successful projects integrate a variety of housing types, public amenities, and affordability frameworks to ensure community support.
6. Exit and Liquidity Scenarios
Investors must account for:
- Demand cycles
- Tenant mix evolution
- Long term operating costs
- Capitalization strategies
Sound exit planning ensures projects remain financially resilient across market cycles.
Conclusion
Smart suburbs represent the next evolution of American community development. By blending suburban space with smart city innovation, developers have the opportunity to create scalable, future ready communities that meet the needs of modern households and employers.
Technology, planning, and community design are converging to build suburban regions that are more connected, more sustainable, and more dynamic than ever before. The suburban frontier is no longer just residential. It is becoming a new kind of urbanism built for a digital era.