Introduction
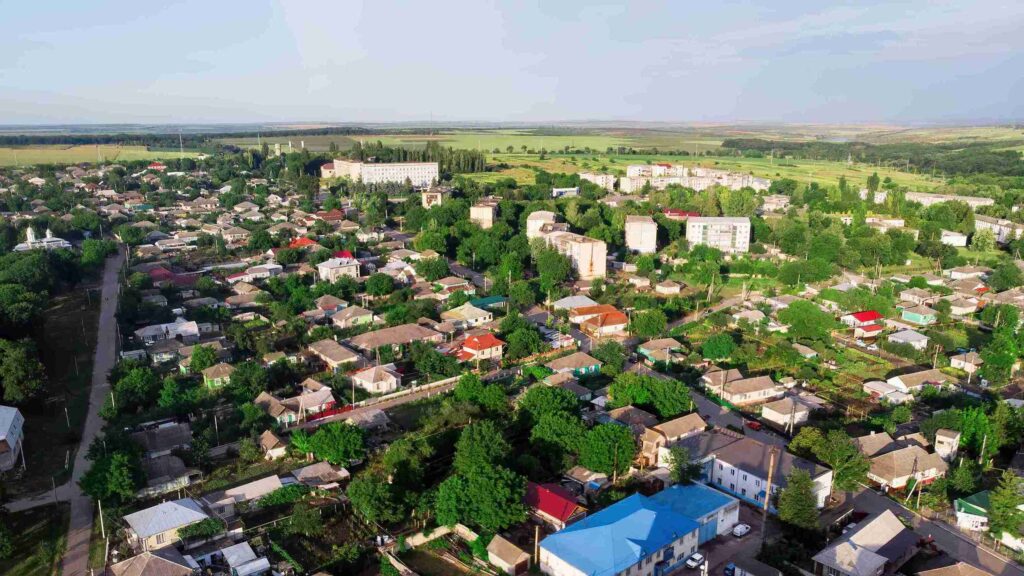
Remote work has permanently reshaped the geography of American housing. What started as a temporary response to the pandemic has become a structural force, influencing where households choose to live, what developers build, and which regions attract long term investment.
By weakening the dependence on daily commutes, remote work allows families and professionals to prioritize affordability, space, and lifestyle. This shift has created a durable wave of migration toward suburbs and lower density counties.
In 2025, these patterns are not fading. Instead, they continue to gather momentum, reinforcing a new residential map that favors communities offering space, connectivity, and value. The suburban resurgence is now a defining component of the modern U.S. housing cycle.
What Is Driving the Suburban Resurgence
Remote Work Enabled
Remote work is the single most powerful catalyst behind the rise of the suburbs. With fewer professionals tied to office locations, households have expanded their search radius for housing.
Research from the Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco shows a direct connection between remote work trends and the rise in housing demand outside major city centers. Their analysis found that remote work was responsible for a significant share of home price growth in suburban and exurban areas during the pandemic period.
Source: Remote Work and Housing Demand
https://www.frbsf.org/research-and-insights/publications/economic-letter/2022/09/remote-work-and-housing-demand/
Even as the economy stabilizes and companies refine hybrid policies, remote work remains deeply embedded in corporate culture. This long term flexibility strengthens the appeal of suburbs where buyers can secure more value for their money.
The Housing Demand Effect
With remote work becoming the norm, household priorities have changed. Families now want:
- Larger interiors
- Additional rooms for offices
- Outdoor space
- More privacy
- Accessible amenities
- Safer, quieter neighborhoods
Urban centers, while vibrant, often cannot deliver these features affordably. Suburbs provide the mix of cost efficiency and lifestyle upgrades that remote workers find attractive. This shift in demand is most evident in counties surrounding fast growing metros, where builders have scaled up construction to meet rising interest.
Migration to Suburbs and Less Dense Counties
Migration trends highlight the scale of the suburban surge. According to the Harvard Joint Center for Housing Studies, migration accelerated in less dense counties from 2020 onward and continues to show strength through 2025, particularly among young families, mid career professionals, and remote enabled workers.
Source: Harvard JCHS Pandemic Migration Report
https://www.jchs.harvard.edu/sites/default/files/research/files/harvard_jchs_pandemic_migration_frost_2025.pdf
This trend is strongest in areas offering:
- Affordable single family homes
- Competitive school districts
- Proximity to major job markets
- Lower taxes and cost of living
- Larger housing supply for new development
Regions in the South, Mountain West, and Midwest have gained the most from these patterns. Many of these same counties were stable or even shrinking before 2020, underscoring how transformative remote work has been.
Data Snapshot: Suburbs on the Move
Remote Work and Housing Demand
Apartment List’s Remote Work Survey shows that most remote workers who moved to suburbs during the pandemic period plan to remain there long term. Many cited affordability, increased space, and improved quality of life as primary reasons for staying.
Source: Apartment List Remote Work Report
https://www.apartmentlist.com/research/remote-work-moving-prefs-survey
Migration Trends
Upwork research reveals that remote workers are the most mobile workforce demographic in the United States, and they continue to drive demand for homes in less dense areas. Their moves are based on lifestyle preferences rather than proximity to traditional job clusters, reinforcing long term suburban demand.
Source: Upwork Remote Worker Mobility Report
https://www.upwork.com/press/releases/economist-report-remote-workers-on-the-move
Residential Sorting Trends
The Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia’s analysis confirms a permanent shift in residential sorting patterns. Remote work has broken the traditional link between geographic job markets and residential decisions. This has redistributed population growth more evenly across suburban and emerging regional markets.
Source: The Great Reshuffle
https://www.philadelphiafed.org/the-economy/regional-economics/the-great-reshuffle-remote-work-and-residential-sorting
Together, these data points make one conclusion clear: the move toward suburbs is structural, not temporary.
Why This Trend Matters for Housing and Real Estate
Affordability and Space Demands
Affordability remains a key factor in the U.S. housing market. Urban housing prices have outpaced income growth for years, prompting many households to look beyond the city for more attainable options. Suburban communities consistently offer:
- Larger homes at more accessible price points
- Lower rent burdens
- Better price to income ratios
- More predictable long term costs
For families seeking to build equity, suburbs provide a stronger financial foundation.
Supply and Demand Realignment
Suburban development pipelines are expanding in response to demand. Builders are completing more single family homes, townhomes, and build to rent units in suburban counties than in urban centers. This shift reflects:
- Better availability of buildable land
- More flexible zoning
- Lower construction barriers
- Clear household demand signals
Urban regions face higher land costs, stricter regulations, and limited space for expansion. Suburbs, on the other hand, can scale more efficiently and deliver the type of homes buyers want.
Infrastructure and Regional Transformation
Suburbs experiencing strong growth are investing heavily in infrastructure. Improvements include:
- Road expansions
- Public transit extensions
- Broadband upgrades
- Healthcare facility growth
- School district investment
- Community amenities
For remote workers, connectivity is essential. Regions with strong broadband and transportation infrastructure gain a competitive advantage in attracting new residents.
A Five Point Checklist for Investors and Developers
Commute Flexibility and Remote Work Indexing
Markets with higher remote work participation often draw stronger suburban migration. Investors should monitor the level of hybrid and remote adoption among major employers in the region, as well as local workforce statistics.
Housing Affordability Gap
A wide affordability gap between urban cores and nearby suburban counties typically signals ongoing momentum. When urban price to income ratios become stretched, buyers look for suburban alternatives that offer more space and lower overall costs.
Population and Migration Flows
Key indicators for evaluating suburban strength include:
- Net inbound migration
- Household formation rates
- Growth in working age residents
- Increased school enrollment
- Suburban building permit trends
These metrics help determine whether demand is cyclical or sustainable.
Local Infrastructure Readiness
The quality of a suburban region’s infrastructure is directly tied to its long term growth potential. Investors should examine:
- Highway access
- Public transit links
- Internet connectivity
- Retail and medical amenities
- Planned public investments
Strong infrastructure supports both residential and commercial expansion.
Supply Risk and Construction Pipeline
Balanced supply is essential for long term return stability. Suburbs with rapid population growth can absorb more supply, while regions with excessive speculative construction may face short term pricing pressure. Evaluating the regional pipeline helps investors anticipate market performance.
Implications and Future Outlook
Remote work has altered the balance between urban and suburban living in ways that will continue shaping the market for years. Even as workplace expectations evolve, the flexibility that remote work offers is now embedded in household decision making.
The suburban outlook remains strong for several reasons:
- Long term demographic shifts favor space rich communities
- Affordable metros are gaining national attention
- Single family homes remain the preferred housing type
- Infrastructure investment continues to favor suburban corridors
- Employers accept distributed workforces
- Families prioritize school districts and neighborhood stability
Suburbs are becoming economic and residential hubs in their own right, not merely extensions of nearby cities.
Conclusion
Remote work has redrawn the U.S. housing map and ushered in a new era for suburban living. Affordability, larger homes, lifestyle preferences, and long term flexibility have aligned to create a demographic and economic shift that is reshaping the market.
For households, suburbs offer attainable space and stability. For investors, they present reliable demand and scalable opportunities. For developers, they provide the land and policy environment needed to meet evolving housing needs.
The suburban resurgence is not a temporary phase. It is a structural transformation that will define the next decade of American housing.